Service:
- web publishing
- instant messaging server
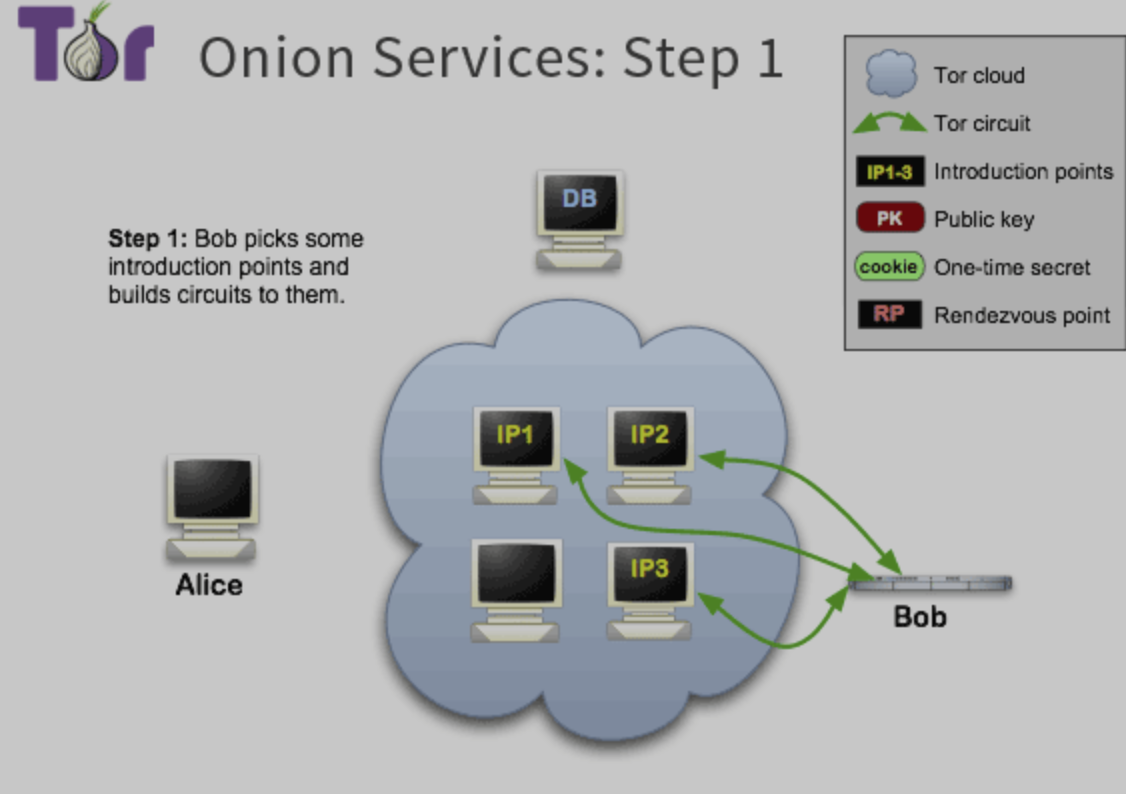
Step 1:
- Service advertise its existence in Tor network before clients be able to cotact it.
- service random找几个relays, build circuit和他们,但不是direct connection; 这几个relays就是introduction points(), service会诉这几个relays自己的PK(Public Key), 但是我们并不想让introduction points知道ip addr, 尽管他们知道PK
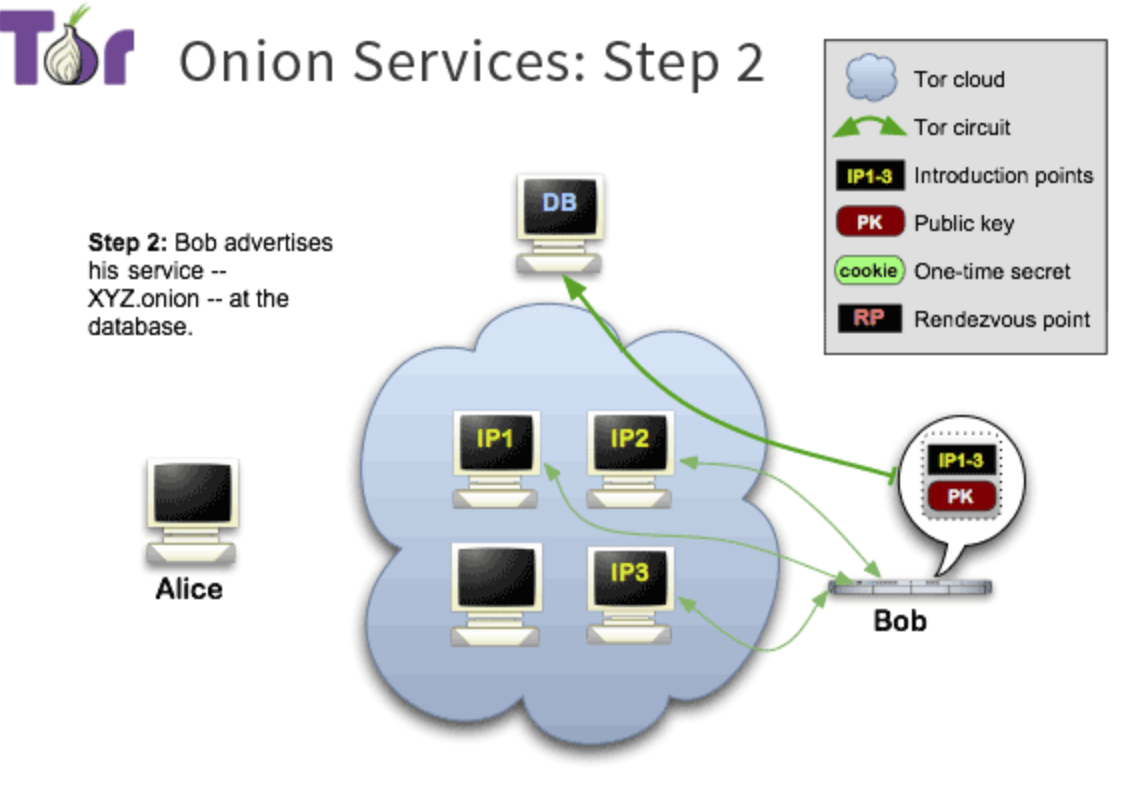
Step 2:
- onion service descriptor: 我们的service装起来一个(assembles)onion service descriptor, 其中包括了: 1.PK;
- summary of each interduction points;
- 并且用private key sign this 含有PK的discriptor
- 之后把这个discriptor传给distributed hash table(DB), The descriptor will be found by clients requesting XYZ.onion where XYZ is a 16 character name derived from the service’s public key. client request一个地址就能找到这个discriptor. (这个名字和PK有一定关系,但是是什么关系还不太清楚)
但是这里面没有任何bob的 地址。
XYZ is an autogenerated name derived from Bob’s public key
Step 3:
client 需要知道onion service的addr, 之后download descriptor, 就知道了introduction points and right public keys to use. client 也会random pick node as(rendezvous point) point by telling them a one-time secret.
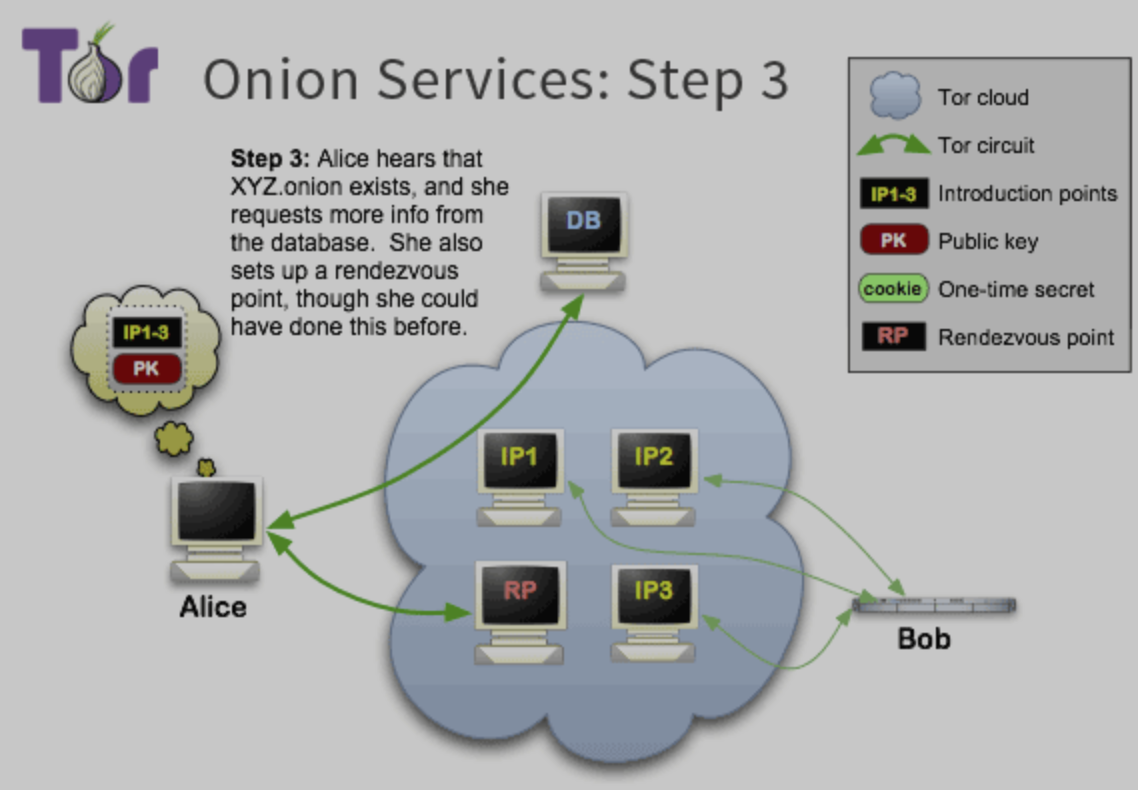
- [] The downloaded advertisement record tells Alice where to find Introduction Points.
- [] She further chooses a random Tor node to act as a Rendezvous Point, and connects to it.
Step 4:
这时候我们有了rendevous point 和 descriptor client造出来一个introduce message(encrypted to the onion service’s public key) including addr of rendezvous point + the one-time secret. 之后把这个message 给其中一个introduction points.
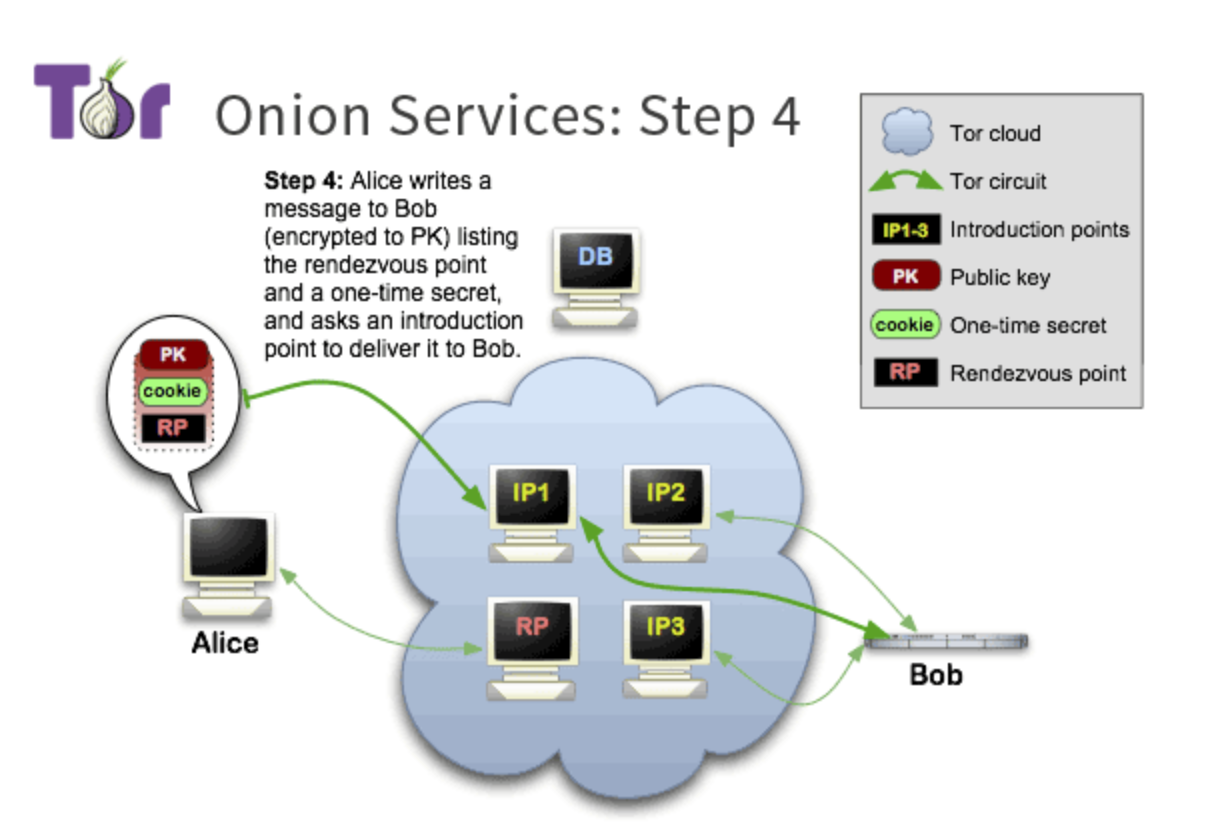
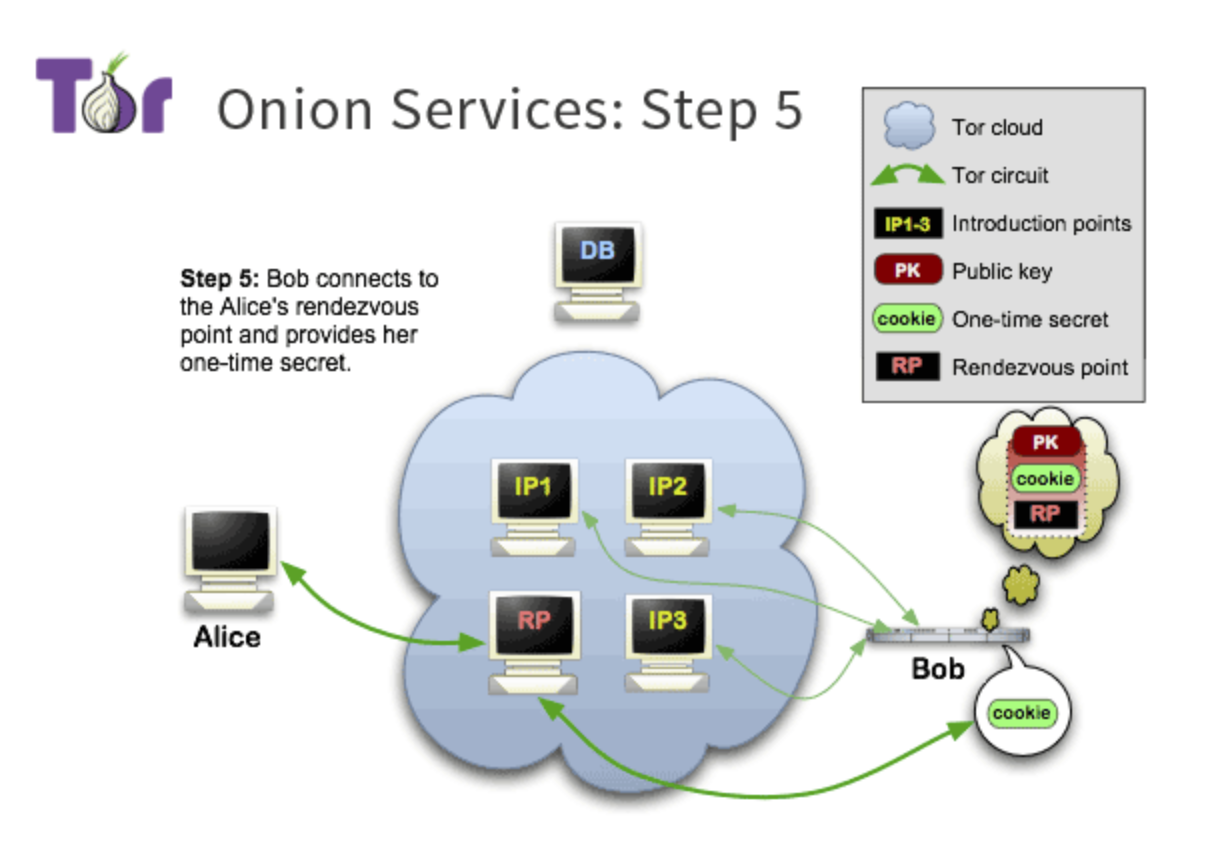
Step5:
等到消息传给onion service 之后, onion service用自己的private key decrpted。 之后就知道了rendezvous point and one-time secret.
之后onion service创建rendezvous msg然后把它给rendezvous point。
记住最开始的几个introduction point很关键。
Step6:
rendezvous point告诉client 成功连接。 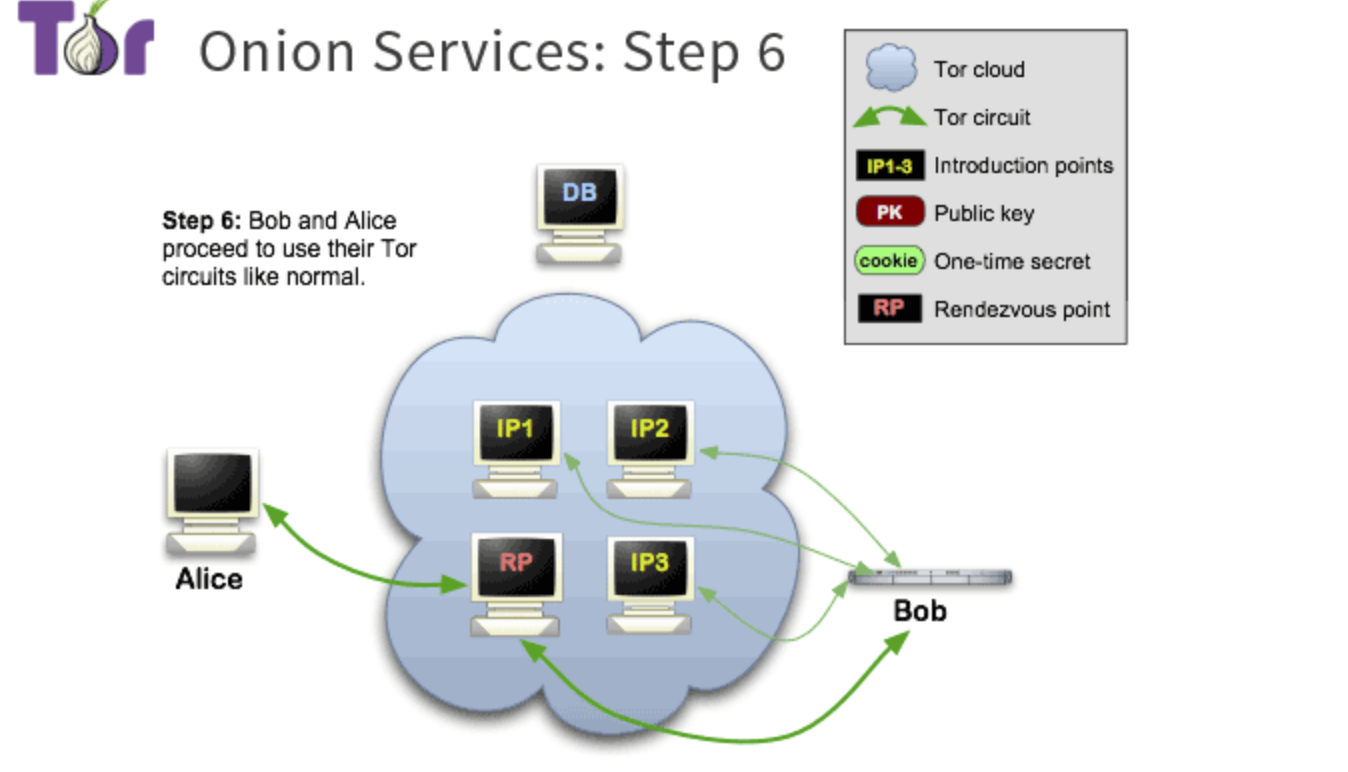
但是Tor还不够完全anonymous:
- Session Cookies, including third party trackers 到处都是
- Browser Reveal you third party:
- 访问nytimes.com, 广告业务模块
window.location.href, 令browser发送get request to 广告网站, 这样广告网站就能用request header得到他想要的信息。
- 访问nytimes.com, 广告业务模块
Tor Browser: All traffic through Tor. Non-tracking search engine.
Browser Fingerprint:
- collect enough information from a client, you can (probably) identify them uniquely • User-Agent string • Screen size • Browser plugin details • Language • Platform • Etc.
- Tor Browser 没有