DynamoDB
Attribute
each item is composed of one of more attributes hash attribute -> partition key range attribute -> sort key
Primary Key
Primary key uniquely identifies an item partition(+ sort key)
Primary key Uniqueness: In a table that has a partition key and a sort key, it’s possible for multiple items to have the same partition key value. However, those items must have different sort key values.
GSI(Global Secondary Index):
naive approch: scan with filter expression; scalable impossible-> latency+cost index as GSI; no need to scan 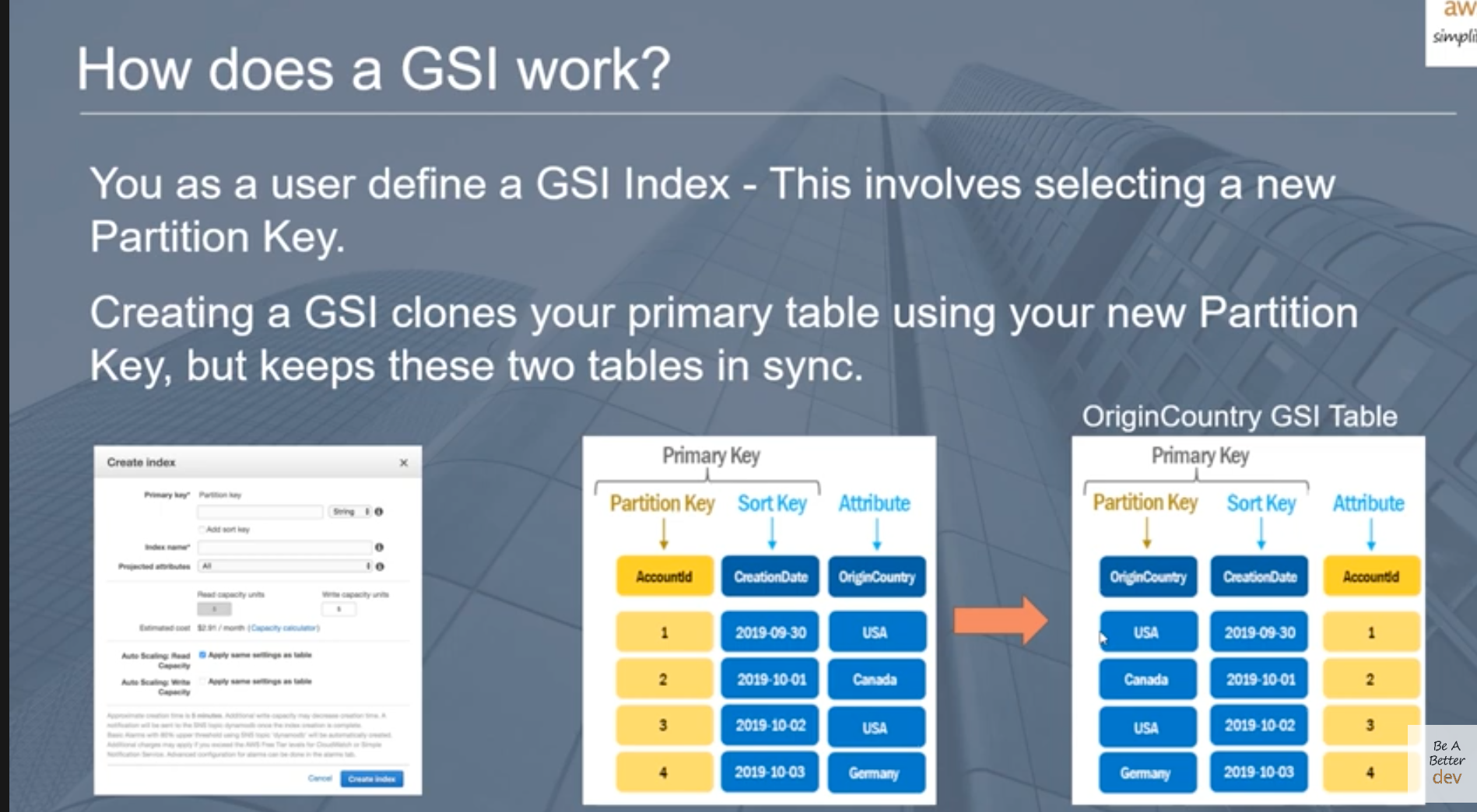
- GSI parition key requires uniform data distribution
- throttling: define RCU/WCU (read/write capacity unit),
- WCU of GSI >= primary table of WCU, when replicate, write to main -> update on all GSI
- write to main table result in a write to the GSI, doubleing the cost of writing
- write to main table are eventually replicated on the GSI, usually very quick but no guaranteed SLA(Service Level Agreement)
- race condition due to nature of eventually consistencty -> GSI can potentially return stale data, when update/delete on primary; do not retrival GSI as truth, may be stale./
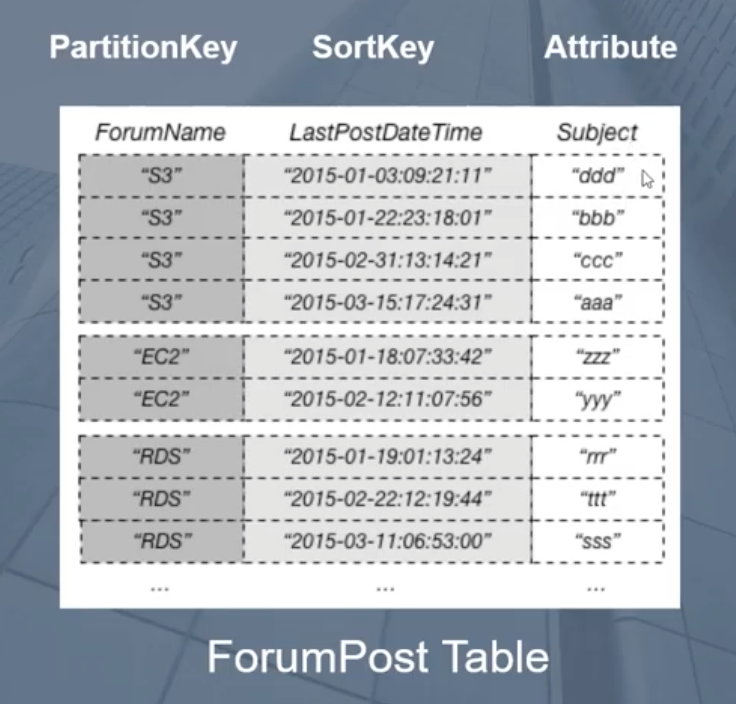
LSI(local secondary index)
 )
)
- index within partition
- one sort key in one table -> several property to lookup
- LSI -> a certain attribute;
Limits:
- can only define a LSI at table creatation time
- limited to 5 LSIs
- no extra cost
LSI v.s. GSI
needs to carefully pick the LSI/GSI performance matters! tradeoff by access pattern read heavy or write heavy LSI: fast write only one 1 partition read needs to fan out to all partitions
GSI: write into multiple partitions for each GSIs lookup very fast