Load Balancing Caching Data Partitioning
load balancing
features:
- spread traffic acorss cluster
- keep track of status of all resources while distributing request
- prevent single point failure
Note: Layer 7 Application traffic: has info from app layer -> by request type to the server
application on 3 places:
user <LB> web server <LB> internal platform/app server/cache server <LB> DB
caching
short term memory locality of reference principle: HW, OS, Web browsers, web app
Application serer cache
for multiple nodes, if the same request is forwarded to different node, the local node cache will not be reused, which increases the cache missing, how to improve this?
- global cache
- distributed cache
CDB Content Delivery Network
large amounts of static media if the system is not large enough to have it’s own CDN, we can ease a future transition by serving the static media off a separate subdomain using lightweight HTTP server like Nginx, and cut-over the DNS from your servers to CDN later. 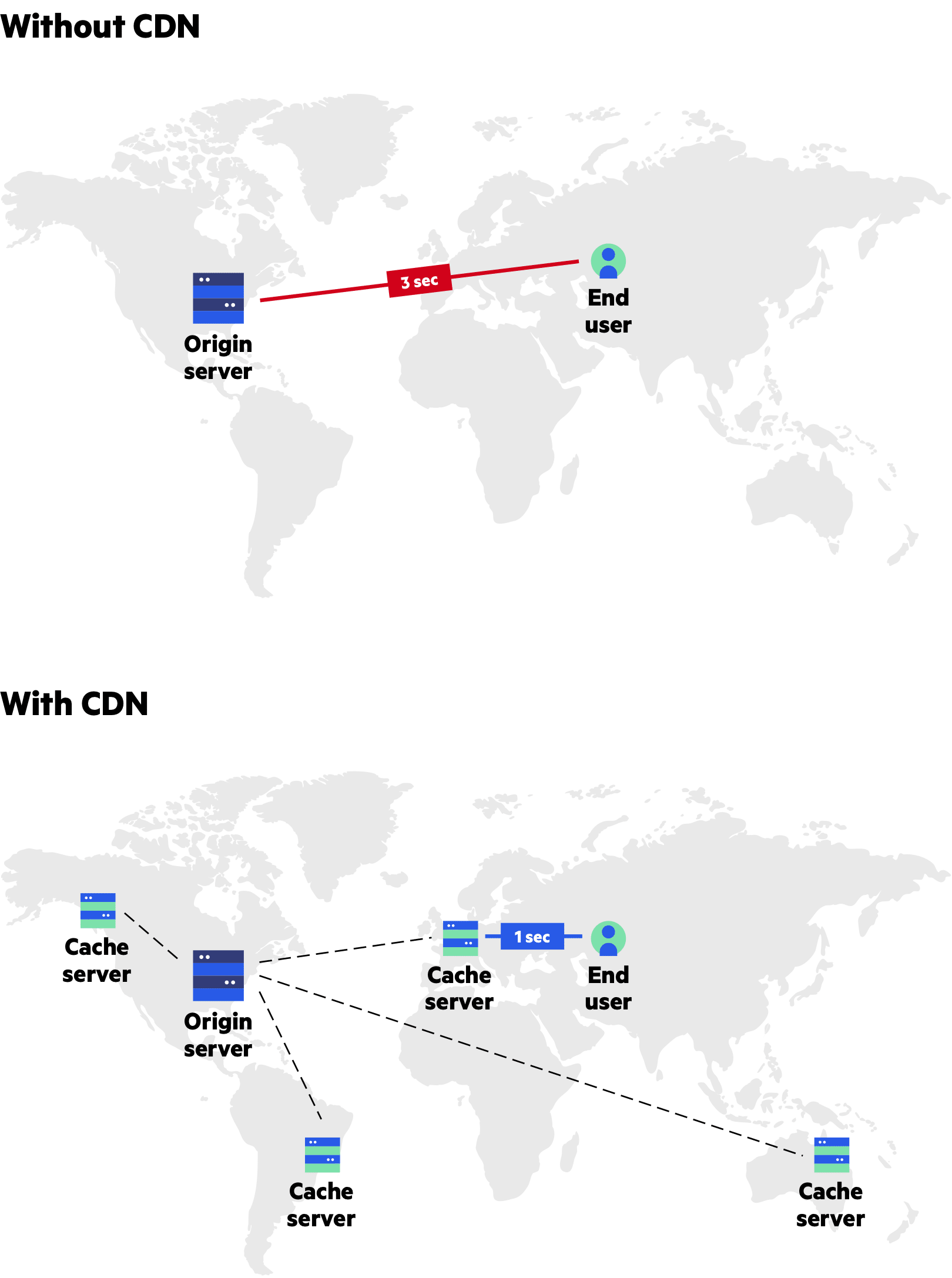
public v.s. private IP: A public IP address identifies you to the wider internet so that all the information you’re searching for can find you. A private IP address is used within a private network to connect securely to other devices within that same network. Each device within the same network has a unique private IP address
why Nginx? route user request to different ports with load balancing can set cache
Apache HTTP server v.s. Nginx c10K? Nginx: Event driver, more used site use the nginx Apache Https: process non blocking
Cache Invalidation
wirte-through cache:
write -> cache -> DB: no data loss: only after two-level write, return success higher latency
write-around cache:
write -> -> DB, bypass the cache suitable: highly write, seldom re-read re-read: -> cache miss
write-back cache
write -> cache ->(certain condition/interval) -> DB -> high throughput && low latency
Cache Eviction policy:
FIFO/LIFO/LRU/MRU/LFU/RR
Data Pertitioning
horizontally scale: big DB/table -> mutiple machines:
Partitioning method:
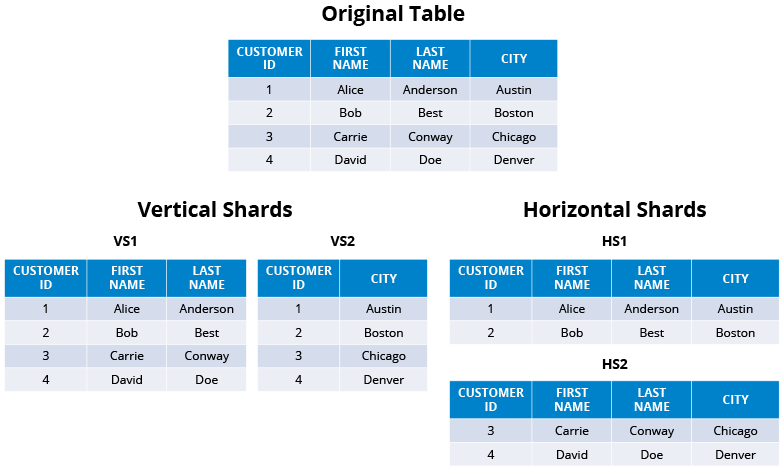
- Horizontal Partitioning(data sharding): imbalanced server load if range not pick carefully
-
Vertically Partitioning: a feature a server if additional growth: for a certain feature, still need to further horizontal partition Straightforward to implement. Low impact on the application
- Dicrectory-based A lookup service for partitioning schema and abstracts it away from the db access code allow DB server to change partition schema without impacting app cons: single point failure.
Partitioning Criteria
a. partition number = hash(keys…) -> partition server cons: server number is fixed; consistent hashing can solve this problem. b. list partitioning: a bunch of key will go to a certain partition server c. round-robin partitioning: uniform data distribution d. composite partitioning: e.g. list + hash -> consistent hashing
data denormalization
: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T3cx09FINuU flattening data, redundant data
Common Problem
Constraints: The fact that operations across multiple tables or multiple rows in the same table will no longer run on the same server a. Join and Denormalization: cons: perform joins that span database partitions -> not efficient denormalize database -> joins on a single table cons of denormalization -> data inconsistency b. referential integrity foreign key: needs application code to enforce, if the RDBMS doesn’t support foreign keys/referential integrity
c
- date imbalanced
- request imbalanced/.